Clocks on the Space Shuttle run slightly slower than reference clocks on Earth, while clocks on GPS and Galileo satellites run slightly faster. The nature of spacetime is such that time measured along different trajectories is affected by differences in either – each of which affects time in different ways.
In theory, and to make a clearer example, time dilation could affect planned meetings for astronauts with advanced technologies and greater travel speeds. The astronauts would have to set their clocks to count exactly 80 years, whereas mission control – back on Earth – might need to count 81 years.The astronauts would return to Earth, after their mission, having aged one year less than the people staying on Earth.
With technology limiting the velocities of astronauts, these differences are minuscule: after 6 months on the International Space Station (ISS), the astronaut crew has indeed aged less than those on Earth, but only by about 0.005 seconds (nowhere near the 1 year disparity from the theoretical example). The effects would be greater if the astronauts were traveling nearer to the speed of light (299,792,458 m/s), instead of their actual speed – which is the speed of the orbiting ISS, about 7,700 m/s.
There are two types of Time Dilation: Relative velocity time dilation and Gravitational time dilation.\
Time dilation: special vs. general theories of relativity
In Albert Einstein's theory of relativity, time dilation in these two circumstances can be summarized:
- In special relativity (or, hypothetically far from all gravitational mass), clocks that are moving with respect to an inertial system of observation are measured to be running more slowly. This effect is described precisely by the Lorentz transformation.
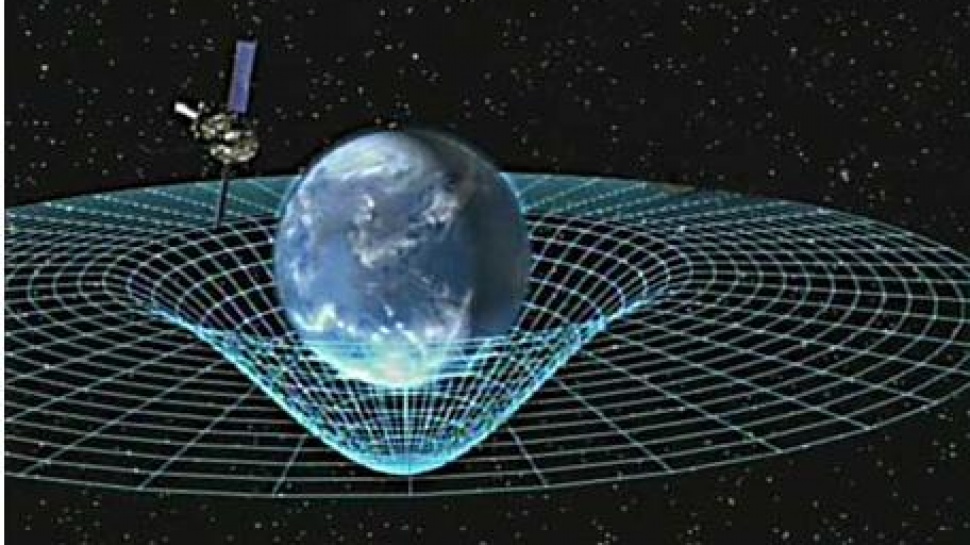
- In general relativity, clocks at a position with lower gravitational potential – such as in closer proximity to a planet – are found to be running more slowly. The articles on gravitational time dilation and gravitational redshift give a more detailed discussion.
There is still some disagreement in a sense, because all the observers believe their own local clocks are correct, but the direction and ratio of gravitational time dilation is agreed by all observers, independent of their altitude.
Science fiction enthusiasts have noted the implications time dilation has on forward time travel, technically making it possible. The Hafele and Keating experiment involved flying planes around the world with atomic clocks on board. Upon the trips' completion the clocks were compared to a static, ground based atomic clock. It was found that 273±7 nanoseconds had been gained on the planes' clocks.
From the frame of reference of a moving observer traveling at the speed v relative to the rest frame of the clock (diagram at lower right), the light pulse traces out a longer, angled path. The second postulate of special relativity states that the speed of light in free space is constant for all inertial observers, which implies a lengthening of the period of this clock from the moving observer's perspective. That is to say, in a frame moving relative to the clock, the clock appears to be running more slowly. Straightforward application of the Pythagorean theorem leads to the well-known prediction of special relativity:
The total time for the light pulse to trace its path is given by:
The formula for determining time dilation in special relativity or velocity is:
The formula for determining time dilation in gravitational time dilation is:






Share the News